There are 113 identified cannabinoids in the marijuana plant. Researchers also say there are hundreds of other compounds, including terpenes and flavonoids. However, the prohibited status of cannabis means research into its properties is limited. We are aware of THC and CBD primarily because they are generally the two most abundant cannabinoids.
It is easy to assume that these are two of the few cannabinoids with potential benefits. In reality, however, the little research that has occurred regarding other compounds paints a different picture.
It is also possible that individual cannabinoids and terpenes have specific uses. There are dozens of non-intoxicating cannabinoids in weed and plenty that could cause a high. Of course, THC aside, there isn’t enough of any intoxicating cannabinoid available to cause this effect by itself.
One cannabinoid that is beginning to garner attention is THCA. In this guide, we look into it and also determine how it differs from THC.
What Is THCA?
Those with any knowledge of cannabis are likely aware of THC. It is the molecule known to produce the famous intoxicating high that so many people love. Modern-day breeders deliberately grow plants with as high a THC content as possible. What many people don’t realize is that the compound is only available in minuscule amounts in raw marijuana.
You can decarboxylate weed it by exposing it to heat. The process of vaporizing or smoking cannabis performs this task automatically. You can also ‘decarb’ by drying and curing the buds. However, this process takes a relatively long time.
THCA is the “precursor” acid to THC. While THC and THCA are nearly identical in terms of chemical structure, they have a few molecular differences. These account for radical changes in the way they affect the brain.
Namely, THCA does not produce any psychoactive, mind-altering effects. This is why you could hypothetically eat a bunch of raw marijuana buds, and hardly get high at all.
Yet THCA is far from inactive regarding the effect that it has on humans. Instead of producing an intoxicating high, for instance, it potentially possesses dozens of therapeutic health benefits. These include analgesic (pain-relieving), anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties.
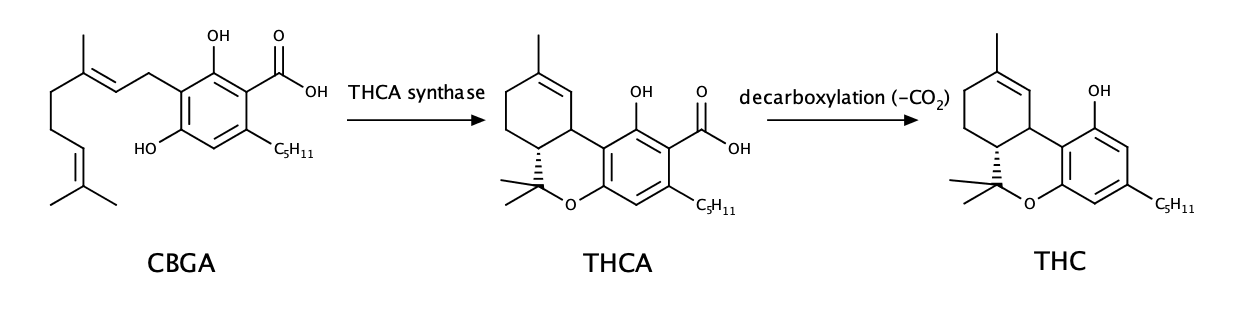
Like every other cannabinoid, THCA comes from CBGA. As plants mature, their enzymes convert the CBGA into one of three cannabinoid precursor cannabinoids: THCA, CBDA, and CBCA.
THC and THCA are similar molecules. However, THCA’s 3D shape means it is too large to fit into the cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB1 receptors. The reason why THC causes intoxication is that it fits into your body’s CB1 receptors.
When THCA gets heated to extreme temperatures (i.e., when you smoke or vaporize it), it becomes THC. It produces a high at this stage.
What Properties Does THCA Possess?
First of all, it is necessary to issue a disclaimer of sorts. There isn’t enough research into THCA to confidently state what it is capable of. That said, the studies which have looked into the cannabinoid provide positive outcomes in general. One suggestion is that THCA stimulates the appetite like THC. It acts as a cannabinoid receptor in itself and has potential neuroprotective benefits.
Here is a more detailed list of the possible properties associated with THCA. Bear in mind, that we need significantly more research:
- Analgesic
- Antiemetic
- Neuroprotective
- Helps with insomnia
- Modulates the immune system
- Anti-inflammatory
There are a few research papers on THCA’s possible benefits. A study by Ruhaak et al., published in Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin in 2011, investigated six cannabinoids. The researchers wanted to evaluate the cyclooxygenase inhibiting effects of these cannabinoids. They found that THCA demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties.
A study by Moldzio et al., published in Phytomedicine in June 2012, looked at THC and THCA. According to the research, THCA could protect against neurodegenerative diseases.
Rock et al. published a study in the British Journal of Pharmacology in July 2013. Researchers found that THCA and CBDA were effective in the reduction of vomiting and nausea. Indeed, their efficacy exceeded that of THC and CBD. The study was on rodents, but it was promising nonetheless.
As you can see by the dates of these studies, however, there is little in the way of recent research. Scientists have a hard enough time trying to get funding for THC and CBD experiments!
What are THCa’s Effects and Benefits?
There isn’t enough research on THCa to definitively state what it can treat and with what degree of efficacy, but preliminary research and anecdotal evidence suggest that THCa will play a pivotal role in cannabis medicine as the industry propels forward. THCa stimulates the appetite like THC; it acts as a cannabinoid receptor agonist (a chemical that binds to a receptor and activates the receptor to produce a biological response), and in so doing helps in its neuroprotective (brain protection) effects, it is also a powerful anti-inflammatory, helps fight cancer and other tumors, aids with sleep, and more. Here are some of the potential benefits studies have started to unveil:

- Analgesic – Relieves pain.
- Anti-Emetic – Reduces vomiting, nausea, and and appetite loss.
- Anti-Inflammatory – Reduces inflammation; for treatment of arthritis and lupus.
- Anti-Insomnia – Aids with sleep.
- Anti-Proliferative – Inhibits cancer cell growth; noted in studies of prostate cancer.
- Antispasmodic – Suppresses muscle spasms.
- Modulates Immune System – THCa has been shown to both improve and potentially suppress the immune system functions.
- Neuroprotective – Slows damage to the nervous system and brain; for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
What’s the best way to take THCA?
So depending on your needs, you can either heat THCA or administer without the heat.
Smoking THCA:
The moment you heat THCA it’s going to transform into a very strong form of THC. So, if that’s what you’re looking for, you’re probably wondering, “How the heck do I smoke it?” You’ll be pleased to know it’s not very difficult: you can dab it, or sprinkle it on a bowl or joint of your favorite flower to amp up the potency. No fancy gear or engineering necessary.
When we tested smoking THCA the main response has been “Woah.” It’s clean hitting, and just in case you’re concerned about taste, when asked to describe it, we got an overwhelming response of, “Like cannabis.” Since the potency is strong, we’ve gotta recommend using caution until you’re confident with your tolerance.
Non-Heat Methods of Administering THCA:
If you don’t want to feel a psychoactive high and are seeking THCA for potential anti-inflammatory effects medicinal purposes, there are a wide range of edible products designed specifically for administering THCA in its raw form, including:
- Juicing: Yes, you can simply juice your raw, fresh cannabis leaves like another vegetable and blend them into a smoothie. This method allows you to extract the most THCA that’s present in the leaves. If you can’t get a constant supply of fresh cannabis fan leaves regularly make a large batch and freeze the juice to defrost at your convenience.
- Tinctures or drops: Raw cannabis tinctures have high levels of THCA. These tinctures are easy to dose and are easier to travel with than juicing.
- Transdermal patches: THCA patches work just like nicotine patches, simply adhere to any veinous (prominent or noticeable veins) part of the skin for 8-12 hours, typically areas like the inside of the wrist or the top of the foot.
- Pre-made edibles: There are a wide variety of THCA edibles on the market. We recommend doing your research, buying from a trusted brand, and ensure that each product comes with a batch number with accompanying test results.
NOTE: We caution against vaping or cooking with THCA as applying heat will start the process of turning it into THC and your dosing may vary greatly because it’s hard to know how much has been converted into THC. Not ideal if you’re seeking a clear-headed mind-set! And like everything to do with cannabis, when you’re more aware of your ideal dosage, you’re more likely to have a positive experience.

In the 60’s and 70’s I could take a few hits off a joint and cure my allergy. My nose would run constantly, watery eyes but two hits off some old fashion weed and boom, cured. Today from the middle of spring until the end of summer I frequently have a hard time getting a full breath of air. But two hits of weed and i can breath again.
Pingback: What are cannabinoids? – Cannabis Media Blog
Thank you for that information. I’ve just infused raw cannabis plant with an avocado and coconut oil. It’s been 3 weeks of setting outside for an hour or so then putting it back into a drawer until the next day. Next I’ll strain it and use it sublingually. Usually I’ll know the strain and it also has CBD properties but this time I’m unaware of any CBD so I was curious if the THCA alone had any benefits. Thank you again for your article.