Physical signs of marijuana use include red eyes, poor muscle coordination, delayed reaction times, and increased appetite. A sudden shift in mood from tense to relaxed could indicate marijuana use, as could abrupt symptoms of anxiety, panic, and/or hallucinations. Marijuana also has a distinctive smell, sometimes described as skunk-like. Catching a whiff of this scent on a person’s clothing or hair could also be a sign that the person has used the drug recently.
At home, at work, or in other places where sobriety is the norm, individuals who are high on marijuana may sometimes go unnoticed.
Oftentimes, people who notice a change in someone may second-guess their initial perception. As part of this process of doubting, people may attribute the concerning behavior to fatigue, illness, or even just an off mood.
As the concerning behavior persists, it becomes more difficult for concerned individuals to deny that there may be a problem. In order to informally investigate if drug abuse is occurring, it’s important to have an understanding of both physical and psychological signs of abuse.
The Effects of Marijuana on the Brain
Most Americans have a general idea about the side effects associated with marijuana use, and these effects are the result of how marijuana acts on the brain. THC is the short-form term for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, which is the psychoactive chemical in marijuana. Blood carries THC to the brain where it acts on cannabinoid receptors (the complexes that interact with the cannabinoid neurotransmitter). Cannabinoids naturally occur in the body.
The general effect of cannabinoids on cannabinoid receptor sites is to slow down communications between the cells in the body and the brain. The presence of THC has a similar effect, which is why marijuana is often associated with a relaxing and calming effect. THC also triggers the brain’s reward system, which results in the pleasurable effects associated with marijuana.
Signs of Use
The short-term effects of marijuana use are also signs of recent use. As the Foundation for a Drug-Free World notes, the following are some common physical side effects associated with marijuana use:
- Panic
- Anxiety
- Poor muscle and limb coordination
- Delayed reaction times and abilities
- An initial liveliness
- Increased heart rate
- Distorted senses
- Red eyes
Methods to Use Marijuana
A marijuana high can generally last up to a few hours. In general, the duration of the high will depend on the user’s level of tolerance, the particular potency of the marijuana, and the way the drug was consumed. The following are some of the most popular ways marijuana is used:
- Smoking it (in a bong or rolling papers)
- In food as “edibles”
- In teas
- In hash or wax form
- In a vaporizer
- In tonics and tinctures
The consumption of marijuana-based edibles can increase the likelihood of adverse reactions. The THC in edibles takes longer to be absorbed into the blood than when marijuana is smoked. As a result, the individual who consumes edible forms of marijuana may overeat to compensate for the lag time in the high, which can be dangerous.
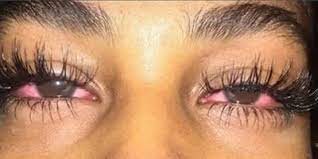
What causes red weed eyes?
If it’s not irritation from smoke that causes your eyes to get red when you indulge, what is it?
The answer lies (mostly) in the way cannabis lowers blood pressure and can dilate capillaries. Marijuana’s effect on blood pressure is the primary reason it is sometimes used to treat glaucoma.
Now, it’s important to keep in mind that while many use cannabis to manage their glaucoma, there have been other studies that contradict its role. For instance, one study found that CBD in marijuana may actually raise eye pressure and worsen glaucoma.
Regardless, we know that when users smoke or ingest weed, they typically experience an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. WeedMaps describes this as comparable to other physical activities, such as exercise.
However, shortly after getting the initial effects from cannabis, heart rate returns to normal and blood pressure begins to lower. Along with lowering blood pressure comes dilation of the blood vessels and capillaries. And that includes the ocular capillaries – in your eyes.
When your ocular capillaries dilate after consuming weed, blood flow increases to the eyes. Additionally, the increased blood flow causes a reduction in intraocular pressure, or fluid pressure inside the eyes. The reduced intraocular pressure is the reason marijuana potentially may help treat glaucoma. Increased blood flow and reduced intraocular pressure also contribute to the appearance of bloodshot eyes.
The reason cannabis can reduce blood pressure and cause bloodshot eyes is because of the cannabinoids present in the plant. Various cannabinoids contribute to different effects.
That’s why it doesn’t matter if you eat, smoke, or vape cannabis. You have the potential to get red eyes if the cannabinoid content is high or potent enough. Specifically, it comes down to the amount of THC in the plant, as not all cannabinoids contribute to lowering blood pressure and thus causing bloodshot eyes.
So, if your edibles get you high, there’s a good chance they’ll also make your eyes red. Have some eye drops on hand if you don’t want your eyes to betray you!
What causes cottonmouth?
While red eyes may be more obvious to observers, you might notice cottonmouth before you even have a chance to look in the mirror. Many people think that cottonmouth, which refers to a dry and sometimes sticky feeling in the mouth, is caused by smoking only. However, much like red eyes, cottonmouth can happen from vaping, consuming tinctures, or eating edibles.
It makes sense to think that smoking specifically causes the mouth to dry out. But that’s not necessarily the case. Many studies have looked at the effects of cannabinoids on salivation without having participants (or rats) smoke. And the consensus is that some cannabinoids can contribute to a decrease in saliva secretion.
A 2006 study set out to find causes of cottonmouth and explain why cannabis causes a decrease in salivation. According to DocMJ, researchers experimented on male rats to determine which cannabinoid receptors were present in salivary glands. They determined that cannabinoid 1 and cannabinoid 2 receptors exist in specific locations in the salivary glands. Then, they found that anandamide (an agonist of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2) attaches to receptors in the salivary glands to cause a sensation known as hyposalivation. Essentially, this means a decrease in saliva production.
We know that cottonmouth happens because when we consume cannabis, certain cannabinoids, such as anandamide, influence activity in the salivary glands to cause a decrease in production.
This decrease in salivation has nothing to do with the rest of the body. It is not indicative of dehydration – even though it may feel like it when it happens. So while you may feel groggy or experience a “weed hangover” after a long night of toking up, you won’t experience the typical “hangover” that is partially associated with dehydration from drinking.
Perhaps the most compelling information that comes from research into cottonmouth is more potential for cannabis to provide therapeutic effects. Scientists believe the information they have gained learning about cottonmouth could lead to new therapies for people with conditions relating to salivation.
How do I get rid of red weed eyes and cottonmouth?
Your best defense against red eyes is using an over-the-counter eye drop. Eye drops are easy to get your hands on and will save you a lot of stress if you frequently find yourself in situations where it’s not ideal to reveal just how much you love cannabis.
Plus, eye drops work extremely fast to clear out any redness and give the appearance of clear, non-intoxicated eyes. If you’re in a pinch, it will only take moments for your eyes to clear up. That’s about as fast of a remedy as you can get.
As far as the cottonmouth goes, drinking water is a great defense against dry mouth. According to DocMJ, chronic cannabis users should pay attention to their oral health, as some risks may be associated with chronic dry mouth. These include lesions, increased yeast, or even periodontal disease.

Other than its psychological effects, including distorted sense of time and feelings of euphoria and paranoia, smoking marijuana also comes with some physiological consequences as well. Dry mouth and red eyes are a few of the most recognizable effects of marijuana use. But what exactly about smoking pot makes your eyes red?
Marijuana decreases blood pressure and expands the eye’s blood vessels, causing the appearance of bloodshot eyes, according to Heathline. The effect mainly comes from the ingredient THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, which enters the circulatory system via the bloodstream, according to the University of Toronto.